We Made Big Improvements to Searching for Relays

Relay Search, formerly known as Atlas, is a web application to learn about currently running Tor relays and bridges. You can search by fingerprint, nickname, country, flags, and contact information and be returned information about advertised bandwidth, uptime, exit policies, and more.
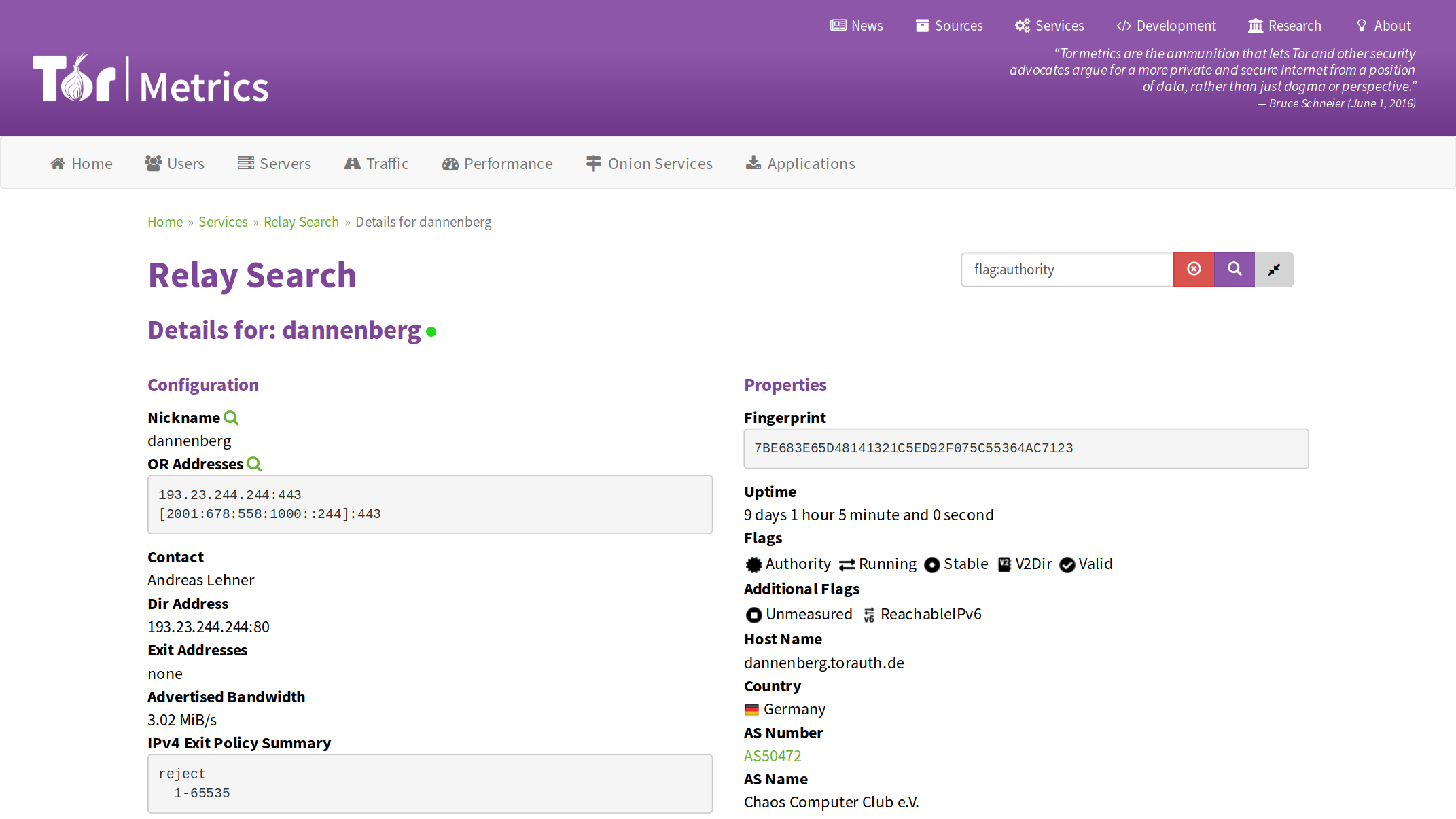
What's New
The biggest change has been the introduction of a new search type: aggregated search.
The aggregated functionality is based on the functionality that Compass provided. Tor Metrics plans to shut down Compass at the end of the year. The Relay Search implementation allows for aggregate searches using the existing search syntax and allows drilling down to further aggregate by other properties, or to display the individual relays in a particular group. The aggregated search results are shown in a table by default but it is also possible to view country-based aggregations in a map view with countries highlighted based on consensus weight, guard/middle/exit probabilities or advertised bandwidth.
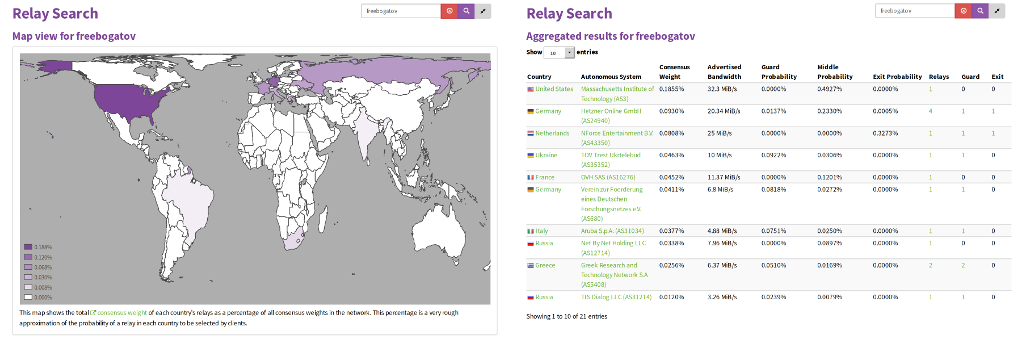
Relay Search shows a number of relays that have been named in honor of Dmitry Bogatov, a software developer under house arrest in Russia for running a Tor exit relay
The "Advanced Search" form will let you explore all the different search parameters that Relay Search offers for both individual relays and for the new aggregated queries.
Finally, we've made a number of other improvements. The highlights are listed here:
- Performance Improvements:
- It is now possible to load up to 2000 relays in a single search query.
- The "Top Relays" page now loads the top 250 relays, not just the top 10.
- New Features:
- UX Improvements:
- Made the bandwidth and IP columns in the search view meaningfully sortable [#15508]
- Merged the theme and branding from the Tor Metrics website to prepare for integration next year [#23518]
- Disabled autocorrect and autocapitalisation to make it easier to search from iOS devices [#23797]
- Disables plotting of graphs when in Tor Browser high-security mode while still providing other details [#19654]
Thanks to the work of Ana Custura, Sebastian Hahn, Mark Henderson, and anonymous contributors for their help in producing patches since I last wrote about improvements in this area. If you have a feature you'd like to see, or if you spot something not working quite correctly, please do feel free to open a ticket about it. If you would like to contribute to fixing some of our existing tickets, we have a guide for contributing to Relay Search.
Comments
Please note that the comment area below has been archived.
Thank you Tor patriots for…
Thank you Tor patriots for your service!
?
?
Great job Tor!!!
Great job Tor!!!
How such tools like atlas…
How such tools like atlas find operating systems of tor relays? I cannot see it in tor consensus file in /var/lib/tor or in replies from tor ControlPort.
Relays publish server…
Relays publish server descriptors, which contain information about the relay such as its nickname, IP addresses and public keys. These also include a "platform" string that indicates the version of tor in use, and the operating system.
OK. Do you mean I need to…
OK. Do you mean I need to enable option
FetchUselessDescriptorsin my tor client and then look at file/var/lib/tor/cache-descriptors? That seems working, but... my tor client started to download that descriptors using 10-20 different Tor nodes, so it doesn't pool these descriptors through my guard nodes. It makes me distinguished among other tor users, which is bad. So, 2 other questions:1) Can I download these descriptors through my entry guard nodes?
2) Will my guard nodes be able to distinguish me from other tor clients because of these fetches? (I don't know, how exactly these descriptors are download, and what's the role of my guards).
Well, problems 1-2 can be mitigated if I use some extra private tor client only used to download full tor descriptors (e.g. via tor-over-tor), but it would be good to have more straightforward solution.
I checked it with google and…
I checked it with google and man torrc, but couldn't find simple answer. Does any tor client need to connect to DirPort of any tor nodes? According to my observations, I have never seen such traffic in my tor client. So, should I forbid these connections in my firewall? (ORPort will be allowed).
Nice
Nice
Thanx All,…
Thanx All,
I love the new interface....
tor bridges connection failed
tor bridges connection failed
After logging into the…
After logging into the latest TorBrowser, why is it that the second relay down in the list (when checking) never changes...no matter how many time I change sites, the relay is still the same. I ran a check on the node displayed and it suspiciously refers to PureVPN which to my knowledge is rather dodgy to say the least. Is someone trying to track me and expose my IP or worse still, have they succeeded?
Sorry but dont know what you…
Sorry but dont know what you want?
Do i need to download…
Do i need to download anything to inprove TOR
I can only use Tor when it…
I can only use Tor when it is updating itself.
Other time it doesn't work. I think it is a bug.
maybe the reason is that I exclude some nodes from some countries. because I am in China.
some Nodes in China don't work correctly.
Hope someone can help me with this problem.